What is Pap smear test, and how is it done?

Routine health check-ups are essential for safeguarding overall health, particularly in the proactive prevention of conditions such as cervical cancer. One of the most essential screenings for women is the Pap smear test.
This straight forward procedure can identify early abnormalities in the cervix, enabling prompt intervention and treatment.
In this blog, we’ll delve into what is Pap smear test entails, its significance, and how it’s performed.
What is Pap Smear Test, and How is it done?
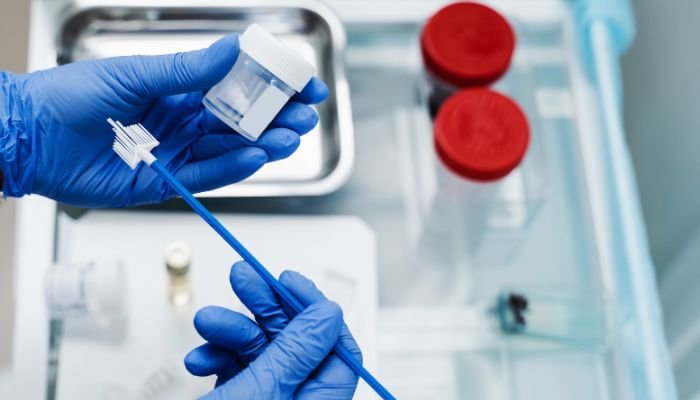
The Pap smear, also referred to as a Pap test, serves as a crucial screening method for cervical cancer detection.
This examination meticulously examines the cervix for any irregularities that may indicate existing cancer or the propensity for cancerous growth.
Conducted by healthcare professionals, a Pap smear involves the collection of cervical cells for microscopic scrutiny, aiming to detect early signs of cancerous changes. Additionally, the test can identify specific infections and instances of inflammation.
Its namesake, Dr. George Papanicolaou, an esteemed American physician, pioneered the development of the Pap smear, revolutionizing cervical cancer detection and prevention.
What can a Pap smear detect?
Pap smears, conducted during pelvic exams, screen for:
- Cervical cancer
- Precancerous cervical cells (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia)
Human papillomavirus (HPV), a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) associated with heightened cervical cancer risk.
How is a Pap Smear Test Performed?
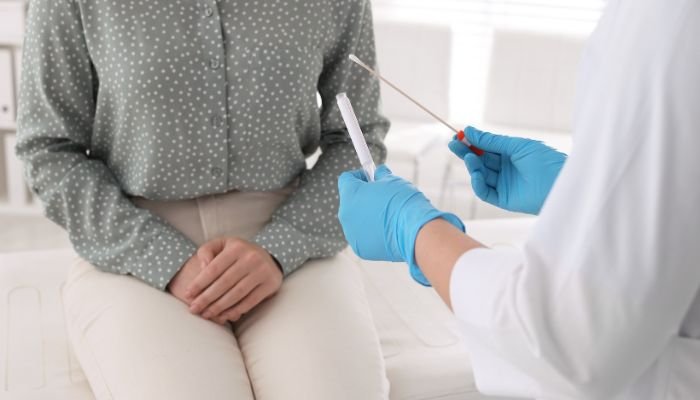
The Pap smear test itself is a quick and relatively painless procedure. Here’s what you can expect during the process:
- Preparation: You may be asked to empty your bladder before the test.
- For optimal test accuracy, please hold off on douching, vaginal creams, and spermicides for 24-48 hours prior to your Pap smear appointment.
- The Procedure: You’ll lie on an examination table, positioning your knees bent and feet resting in stirrups during the procedure.
- Using a lubricated speculum, the doctor gently opens the vaginal walls to access the cervix. Subsequently, a soft brush or spatula is employed to gather a small cell sample from the cervix’s surface.
- This sample is then transferred to a slide and dispatched to a laboratory for microscopic examination. The entirety of the procedure usually lasts just a few minutes.
- After the Test: You may experience some mild cramping or spotting after the test, but this is usually temporary and nothing to be concerned about.
Is Pap smear painful?
While Pap smears aren’t typically painful, they can be uncomfortable. Your doctor may encourage relaxation or engage in casual conversation to ease tension, facilitating easier speculum insertion.
Sensations of the speculum in the vagina are familiar but shouldn’t cause pain. The procedure is brief, lasting only a few minutes.
Light bleeding after pap smears may occur occasionally, but it’s usually short-lived. If bleeding does occur, it’s advisable to abstain from sexual intercourse for 24 hours following the Pap smear.
Frequency of Pap Smear Tests
The recommended frequency of Pap smear tests can vary depending on age, health history, and sexual activity. Here are some general guidelines:
- Ages 21-29: Pap test every three years
- Ages 30-65: Pap test alone every three years
OR
Combination of Pap test and HPV test (co-testing) every five years.
- Ages over 65: Generally, Pap smears may not be necessary if you have had average results previously and have not had any risk factors for cervical cancer. However, discuss with your doctor to determine your best course of action.
What happens after a Pap Test?
The laboratory will analyze the Pap smear sample for abnormal cells. The results can be categorized as follows:
- Normal: No abnormal cells are found. This is the most common result
- Abnormal: Abnormal cells are detected. The type and degree of abnormality will determine the next steps. This may involve a colposcopy, a closer examination of the cervix with a magnifying instrument, or further testing to determine the severity of the abnormality.
What follow-up tests might I need after an abnormal Pap smear result?
If your Pap smear results are abnormal, your healthcare provider may perform a colposcopy or repeat the Pap smear in a few months. Pap smears are screened for abnormalities but not for cancer diagnosis.
A colposcopy involves using a colposcope to examine the cervix and vagina lining, taking tissue samples from any suspicious areas for lab testing. This screening tool is highly effective, with over 95% of treated precancerous cells preventing cervical cancer development.
Additionally, during a Pap smear, your provider may test for HPV, an STI linked to cervical cancer risk. An abnormal Pap smear doesn’t necessarily mean cancer; your provider can discuss findings and next steps.
The Importance of Regular Pap Smear Tests
Routine Pap smears play a vital role in women’s preventive healthcare, as they facilitate early identification of cervical cancer, which is pivotal for effective treatment outcomes.
According to the American Cancer Society, Pap tests have significantly reduced cervical cancer rates and deaths from the disease.
Here are some key reasons why regular Pap smears are essential:
- Early Detection: Detecting abnormal cells before they turn cancerous allows for early treatment with minimal intervention.
- Preventable Disease: Cervical cancer is largely preventable through regular Pap smears and HPV vaccination.
- Peace of Mind: Regular Pap tests can provide peace of mind by knowing your cervical health status.
Pap smears, also known as Pap tests, are crucial for detecting abnormal cervical cells that may lead to cervical cancer.
Consult Dr. Mustafa Aldam, a highly experienced board-certified obstetrician and gynecologist in Dubai, particularly if you’re between 21 and 65 years old, to ensure you stay current with your screenings.
With over 20 years of experience, Dr. Mustafa Aldam specializes in obstetrics, cosmetic, and laparoscopic gynecology surgery.
He is known for his holistic approach to women’s health and actively participates in national and international conferences on obstetrics and gynecology. Dr. Mustafa practices at Al Zahra Hospital Dubai and is recognized as one of the top ObGynae specialists in Dubai.
