How to Detect Ovarian Cancer?

Ovarian Cancer, also often known as “silent killer”, progresses slowly with very few noticeable symptoms in its early stages. This can make detection challenging. However, detecting ovarian cancer in its early stages is crucial for timely treatment and improved outcomes. The condition occurs with vague symptoms or may remain asymptomatic until later stages. Thus, understanding potential signs and risk factors can aid in timely diagnosis.
Routine screenings, such as pelvic exams and imaging tests, play a vital role in diagnosing ovarian cancer early. In this guide, we’ll explore the various methods and strategies for identifying ovarian cancer symptoms and causes, empowering individuals to prioritize their health and well-being.
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer arises when irregular cells in the ovaries or fallopian tubes undergo uncontrolled proliferation.
The ovaries, integral to the female reproductive system, are small, rounded organs responsible for egg production during a woman’s reproductive years. Ovarian cancer originates within these structures. Detecting it can be challenging as symptoms frequently manifest in advanced stages. Treatment typically encompasses surgical intervention, chemotherapy, and other conventional cancer therapies.
What are the possible causes of Ovarian Cancer?
The exact reason behind ovarian cancer is still unclear, although certain factors have been associated with an elevated risk of the disease. Individuals with specific characteristics may have a slightly heightened susceptibility to developing ovarian cancer.
However, some of the ovarian cancer causes could be:
- Advanced age, particularly being over 60 years old
- Obesity
- A familial history of ovarian cancer, where relatives have previously been diagnosed with the condition, or the inheritance of genetic mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, or Lynch syndrome
- Nulliparity or delayed childbearing
- Presence of endometriosis
Moreover, the risk of ovarian cancer tends to increase with age.
What are the symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?
During the early stages of ovarian cancer, symptoms may not manifest, and if they do, they are often mistaken for other prevalent conditions.
Common ovarian cancer symptoms can encompass:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Rapid satiety while eating
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pelvic discomfort
- Fatigue
- Lower back pain
- Alterations in bowel patterns, like constipation
- Increased frequency of urination
Methods of Detecting Ovarian Cancer
Screening tests and examinations serve to identify diseases like cancer in individuals who exhibit no symptoms. For instance, a mammogram can diagnose breast cancer in its earliest stage, even before a palpable mass is detected by a physician.
Considerable research has been conducted to devise a screening test for ovarian cancer; however, progress has been limited. The two primary tests utilized for ovarian cancer screening, in addition to a comprehensive pelvic examination, are transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and the CA-125 blood test.
TVUS, or transvaginal ultrasound
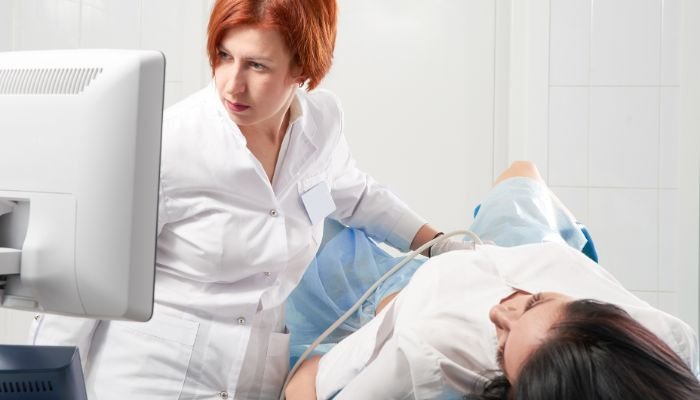
This method uses sound waves to visualize the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries by inserting an ultrasound wand into the vagina. While this test can identify ovarian masses (tumors), it cannot definitively determine if a mass is malignant or benign. When used for screening purposes, the majority of identified masses are non-cancerous.
CA-125 blood test
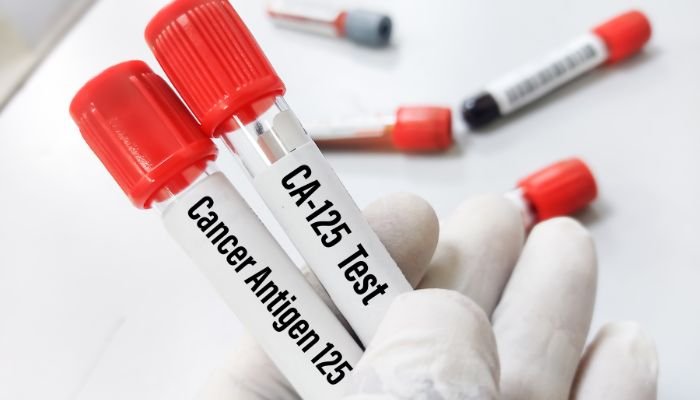
This screening technique quantifies the level of a protein known as CA-125 in the bloodstream. Elevated CA-125 levels are often observed in many women with ovarian cancer. While this test can be valuable as a tumor marker to guide treatment in known cases of ovarian cancer, its effectiveness as a screening tool remains limited. Elevated CA-125 levels are frequently attributable to common disorders like endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease, and not all ovarian cancer cases exhibit heightened CA-125 levels. In cases where an individual without known ovarian cancer exhibits abnormal CA-125 levels, the physician may opt to repeat the test to confirm the results’ accuracy and may consider ordering a transvaginal ultrasound examination.
For people who are at average risk
Women without symptoms and who are not at a heightened risk of developing ovarian cancer are not advised to undergo screening tests. Studies involving women with average ovarian cancer risk found that screening with transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and the CA-125 blood test resulted in increased testing and sometimes unnecessary surgeries without a reduction in ovarian cancer-related mortality. Consequently, major medical and professional organizations do not endorse the routine use of TVUS or the CA-125 blood test for ovarian cancer screening in women at average risk.
For individuals considered to be at high risk
Certain organizations suggest that women at high risk of ovarian cancer, such as those with Lynch syndrome, BRCA gene mutations, or a significant family history of breast and ovarian cancer, may be offered screening with TVUS and CA-125. However, even in this population, it remains unproven whether utilizing these screening tests reduces the risk of ovarian cancer-related mortality.
Screening for germ cell tumors/stromal tumors
No recommended screening tests exist for germ cell tumors or stromal tumors. Some germ cell cancers produce specific protein markers, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), which can be detected in the blood. Following surgical and chemotherapeutic treatment of these tumors, blood tests for these markers can assess treatment efficacy and monitor for cancer recurrence.
Importance of Regular Examinations
During a pelvic examination, a healthcare provider examines the ovaries and uterus to assess their size, shape, and texture. While pelvic exams can aid in the early detection of certain female cancers, detecting early-stage ovarian tumors through palpation alone is often challenging. Nonetheless, pelvic exams may still detect other types of cancers or female health conditions. It is advisable for women to discuss the necessity of pelvic exams with their healthcare provider.
Screening tests utilized for cervical cancer, such as Pap tests or HPV (human papillomavirus) tests, are not reliable for detecting ovarian cancer. Although rare instances of ovarian cancer detection via Pap tests exist, these cases typically involve advanced-stage cancers.
Did you know?
When ovarian cancer is detected at an early phase, approximately 94% of patients survive beyond five years following diagnosis.
What are the different options for ovarian cancer treatment?
Typical treatments for ovarian cancer include:
- Surgery – This procedure usually entails the removal of affected reproductive organs and any cancerous tissue. Surgical methods may involve laparoscopy, a minimally invasive approach, or laparotomy, which requires an abdominal incision.
- Chemotherapy – Your healthcare provider may recommend chemotherapy as a pre-or post-operative treatment. These medications are formulated to specifically target and eradicate cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered intravenously or orally.
- Targeted therapy – This treatment approach employs medications to identify and combat cancer cells by altering their growth and division processes.
- Radiation therapy – While not commonly used, radiation therapy may be considered a treatment option for ovarian cancer in some cases.
Awareness and regular screenings are the key to early detection and the right treatment for Ovarian Cancer
Consult our ObGyn specialist, Dr. Mustafa Aldam via whatsapp
Undergoing regular screenings are essential steps in achieving early detection and receiving appropriate treatment. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can significantly improve their chances of successful outcomes. For expert guidance and personalized care, consult with our experienced ObGyn specialist, Dr. Mustafa Aldam. Your health and well-being are our top priorities, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
