Fibroids vs cysts - How are they detected?

Are you experiencing discomfort or unusual symptoms in your pelvic area? If so, it’s essential to understand the difference between fibroids vs cysts in the uterus. Both conditions can cause likewise symptoms, but they are distinct in their characteristics and treatment options.
Let us shed some light on fibroids vs cysts, including how they are detected, their symptoms, and available treatment options. Understanding these conditions is crucial for seeking appropriate medical care, whether you’re dealing with fibroids or cysts in the uterus.
What are fibroids?
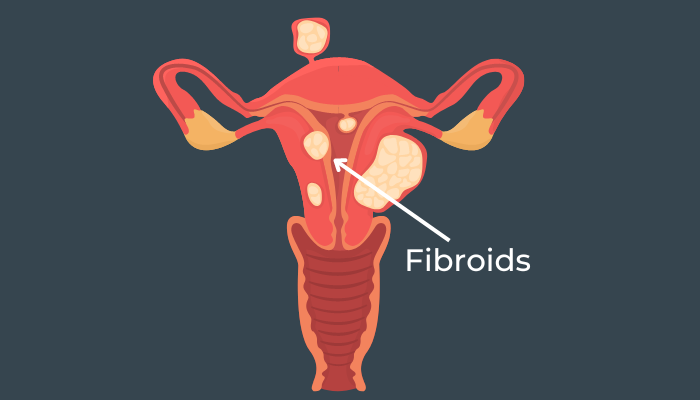
Fibroids, also commonly termed as uterine fibroids or leiomyomas, are benign (non-cancerous) growths that develop in the uterus. They are made up of muscle tissue and can differ in size from small seedlings to large masses. While the cause of fibroids is obscure, hormonal imbalances and genetic factors may play a role in their development.
Fibroids can develop within the wall of the uterus (intramural), protrude into the uterine cavity (submucosal), or attach to its outer surface (subserosal). Some women may have multiple fibroids while others may only have one.
What are cysts?

Cysts are sacs that are fluid-filled and can grow in various parts of the body. They can form on the surface or inside organs, such as the ovaries, kidneys, liver, and breasts. These sacs are typically noncancerous and may vary from small to large.
- Ovarian cysts are one of the most common cysts found in women. They usually develop during ovulation when an egg is released from the ovary. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and disappear on their own within a few months.
- Kidney cysts, however, often result from a genetic condition called polycystic kidney disease (PKD). This disorder causes numerous fluid-filled cysts to develop in both kidneys over time.
- Breast cysts can also occur and may cause breast lumps or tenderness. Although they are generally benign, a healthcare professional should evaluate any new lump to rule out cancer.
Fibroids vs cysts – How are they detected?
Fibroids and cysts are common conditions affecting women’s reproductive health. Detecting these conditions is crucial to seek appropriate treatment.
Regarding fibroids, a healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to feel for any abnormalities in the uterus. They may also use imaging tests such as ultrasounds or MRIs to get a clearer picture of the size and location of the fibroids.
On the other hand, detecting cysts typically involves similar methods. A pelvic exam can help identify any unusual masses or growths on the ovaries. Imaging tests like ultrasounds may be used further to evaluate the size and characteristics of the cyst.
Note: In some cases, additional diagnostic procedures such as blood tests or biopsies may be necessary to confirm whether the growth is a fibroid or a cyst. Early detection plays an essential role in managing both fibroids and cysts effectively!
Also Read: What size of ovarian cyst is dangerous?
Fibroids vs cysts symptoms
Fibroids and cysts may both occur in the reproductive organs, but they have distinct symptoms that can help differentiate between the two conditions.
Symptoms of Fibroids:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Constipation or urinary incontinence (if fibroids press on nearby organs)
Symptoms of Cysts:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Pelvic pain before or during menstruation
- Painful intercourse
- Irregular periods
- Sudden, severe pain if a cyst ruptures
- Nausea and vomiting (if a cyst ruptures)
These symptoms can vary and may not be exclusive to fibroids or cysts. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns, it is recommended to consult a professional for correct evaluation and diagnosis.
Also Read: What size of Uterus Fibroids is dangerous?
Fibroids vs cysts – Treatment
Treatment Options for Fibroids:
Watchful waiting: Monitoring the fibroids for changes in size and symptoms without immediate intervention.
Medications: Prescribing medications such as hormonal birth control, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, or progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) to help manage symptoms and reduce the size of fibroids.
- Non-invasive procedures:
- Uterine artery embolization (UAE): Blocking the blood supply to the fibroids to shrink them.
- Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MRgFUS): Using ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the fibroids.
- Minimally invasive procedures:
- Myomectomy: Removing the fibroids while preserving the uterus, which is suitable for women who wish to retain their fertility.
- Endometrial ablation: Destroying the lining of the uterus to reduce menstrual bleeding caused by fibroids.
- Surgical intervention:
- Hysterectomy: Removing the uterus, and in some cases, the ovaries as well, which is typically recommended for severe symptoms or when fertility is no longer desired.
Treatment Options for Cysts:
Observation: If the cyst is small and not causing any symptoms, doctors may choose to monitor it through regular check-ups.
Medications: Prescribing hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, to regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent new cysts from forming.
- Surgical intervention:
- Cystectomy: Removing the cyst while preserving the affected ovary, which is a common approach for noncancerous cysts.
- Oophorectomy: Removing one or both ovaries, which may be necessary if the cyst is cancerous or there is a high risk of ovarian cancer.
Also Read: Understanding Ovarian Cyst Removal: How Soon Can You Get Pregnant After The Procedure?
Drainage or aspiration: Draining fluid from the cyst using a needle guided by ultrasound, typically performed for larger cysts or those causing significant pain.
Consult Dr. Mustafa Aldam for effective Fibroids vs cysts treatment
If you are experiencing symptoms related to fibroids or cysts, it is important to seek professional medical help. Dr. Mustafa Aldam is a renowned expert in the field of gynecology and specializes in the treatment of fibroids vs cysts. With his extensive knowledge and experience, he can provide you with effective solutions for managing these conditions.
So if you’re experiencing any symptoms associated with fibroids or cysts – such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or fertility issues – don’t delay seeking medical advice.
